2.1 Buying Criteria
Customers within each market segment employ different standards as they evaluate products. They consider four buying criteria: Price, Age, MTBF (reliability), and Positioning.
2.1.1 Price
Each segment has different price expectations. For example, Low End customers seek inexpensive products while High End customers, who need premium products, are willing to pay higher prices.
2.1.2 Age
Each segment has different age expectations, that is, the length of time since the product was invented or revised. High End customers want brand new technology while Traditional customers prefer technology that has been in the market for a few years (see 4.1.4 A Sensor’s Age).
2.1.3 MTBF (Mean Time Before Failure) or Reliability
MTBF (Mean Time Before Failure) is a measure of reliability. Each segment has a different MTBF criteria. Performance customers are extremely interested in high MTBFs while Low End customers are satisfied with lower MTBFs.
2.1.4 Positioning
Sensors vary in their dimensions (size) and the speed/sensitivity with which they respond to changes in physical conditions (performance). Combining size and performance creates a product attribute called positioning.
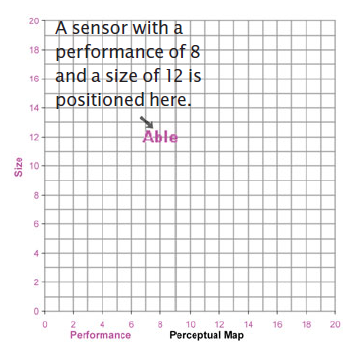
The Perceptual Map
Positioning is such an important concept that marketers developed a tool to track the position of their products and those of their competitors. This tool is called a Perceptual Map. Note the Perceptual Map in Figure 2.1. You will see this map quite often through the course of the simulation. The map measures size on the vertical axis and performance on the horizontal axis. The arrow points to a product called Able with a performance of 8 and a size of 12.
 2 The Sensor Industry
2 The Sensor Industry