3.1.1 Positioning Score
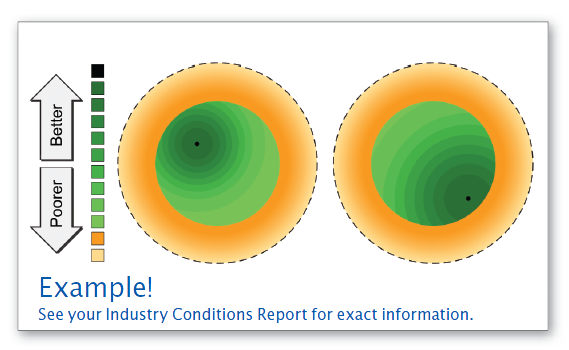
Marketers must understand both what customers want and their boundaries. In terms of a product’s size and performance (as discussed in “Section 2.1.5”), the Perceptual Map illustrates these ideas with circles. Each segment is described with a dashed outer circle, a solid inner circle and a dot representing the ideal position called the ideal spot (Figure 3.1).
Rough Cut Circle
The dashed outer circle defines the outer limit of the segment. Customers are saying, “I will NOT purchase a product outside this boundary.” We call the dashed circle the rough cut boundary because any product outside of it “fails the rough cut” and is dropped from consideration. Rough cut circles have a radius of 4.0 units.
Fine Cut Circle
The solid inner circle defines the heart of the segment. Customers prefer products within this circle. We call the inner circle the fine cut because products within it “make the fine cut.” Fine cut circles have a radius of 2.5 units.
Ideal Spot
The ideal spot is that point in the heart of the segment where, all other things being equal, demand is highest.
Segment Movement
Each segment moves across the Perceptual Map a little each month. In a perfect world your product would be positioned in front of the ideal spot in January, on top of the ideal spot in June and trail the ideal spot in December. In December it would complete an R&D project to jump in front of the ideal spot for next year.
Positioning Rough Cut
Products placed in the rough cut area (orange rings, Figure 3.1) are between 2.5 and 4.0 units from the center of the circle. Products here are poorly positioned and they will have reduced customer survey scores. The farther they are from the fine cut circle, the more the scores are reduced. Just beyond the fine cut, scores drop 1%.
Halfway across the rough cut, scores drop 50%. Scores drop 99% for products that are almost to the edge of the rough cut. Sensors that are about to enter the rough cut can be revised by Research & Development (see “4.1.1 Changing Performance, Size and MTBF”). The location of each segment’s rough cut and fine cut circles as of December 31 of the previous year appears on page 11 of the Courier.
Positioning Fine Cut
Products inside the fine cut (green areas, Figure 3.1,) are within 2.5 units of the center of the circle. Ideal spots for each segment are illustrated by the black dots. The example on the left illustrates a segment that prefers proven, inexpensive technology. The ideal spot is to the upper left of the segment center, where material costs are lower. The example on the right illustrates a segment that prefers cutting-edge technology. The ideal spot is to the lower right of the segment center, where material costs are higher (see Figure 4.1 for an illustration of material positioning costs).
Participants often ask, “Why are some ideal spots ahead of the segment centers?” The segments are moving. From a customer’s perspective, if they buy a product at the ideal spot, it will still be a cutting edge product when it wears out. For contrast, if they buy a product at the trailing edge, it will not be inside the segment when it wears out.
A product’s positioning score changes each month because segments and ideal spots drift a little each month. Placing a product in the path of the ideal spot will return the greatest benefit through the course of a year.
 3 The Customer Survey Score
3 The Customer Survey Score