This practice exercise will help you understand the relationships between business strategy, tactics, functional alignment, and the Foundation® simulation. We will use the Digby Company for this example. (During the practice rounds, each company is assigned a different strategy.)
Printable PDF Version for Distribution to Participants
You will execute your plan by inputting the decisions described below. At the same time, your competitors will execute their assigned plans. The practice exercise will take three rounds As each round is processed, you will evaluate the results and then input the next round's assigned decisions.
Upon completion of the practice rounds, the simulation will be reset to the beginning. You can then create and implement your own strategic plan for the actual competition.
We will adopt a Broad Differentiation Strategy. We will gain a competitive advantage by distinguishing our products with an excellent design, high awareness, easy accessibility, and new products. We will develop an R&D competency that keeps our designs fresh and exciting. We will price above average. We will expand capacity as we generate higher demand.
Premium products for the industry: When only the best will do. Our primary stakeholders are customers, stockholders, management, and employees.
We will allow our present product to become a Low Tech product as the segments drift, eventually investing enough R&D to keep it at the cutting edge of the Low Tech segment. We will introduce new products to ultimately have multiple leading-edge High Tech products and multiple leading-edge Low Tech products.
We will spend freely in promotion and sales. We want every customer to know about our superb designs, and we want to make our products easy for customers to find. We will price at a premium.
We will grow capacity to meet the demand that we generate, avoiding overtime when possible. After our products are well positioned, we will investigate moderate increases in automation levels to improve margins, but never at the expense of our ability to reposition products and keep up with segments as they move across the perceptual map.
We will finance our investments primarily through stock issues and cash from operations, supplementing with bond offerings on an as needed basis. When our cash position allows, we will establish a dividend policy and begin to retire stock. We are somewhat adverse to debt, and prefer to avoid interest payments. We expect to keep assets/equity (Leverage ) between 1.5 and 2.0.
Follow the decision guidelines below unless directed otherwise by your instructor. After the practice rounds, you are free to pursue any strategy you wish, and can abandon the Broad Differentiation strategy entirely.
Daze - Slightly reduce reliability (MTBF) to reduce material cost. Example: Reduce MTBF to 19500.
First New Product - Launch a new Low Tech product, with a project length less than 2 years (no later than December of next year). Example: Name: Dabble (replace the first NA in the list), performance 6.0, size 11.4 and a reliability (MTBF) 18000.
Important: Under the rules of the simulation, the names of all new products must have the same first letter as the name of the company.
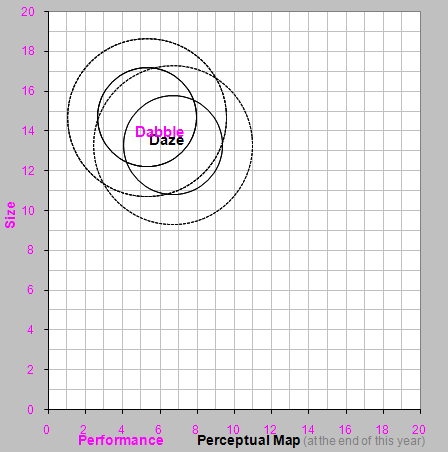
Perceptual Map from the Research & Development Spreadsheet: Product names in black indicate the product's current location, names in magenta indicate the product's revised position (with slight revisions, the names will overlap). Names of newly invented products appear in magenta.
Daze - Make moderate price increase and increase promotion and sales budgets. Forecast unit sales near last year's level. Example: Price $34.75, promotion and sales budgets of $1150 and a sales forecast 1200.
New Product - Marketing decisions will be made next year when the product is ready to begin production.
Production schedules will plan for eight weeks of inventory. That is, have enough inventory on hand to meet demand eight weeks beyond the sales forecast. This requires a 15% inventory cushion (8/52 = 0.15). For example, suppose Marketing forecasts demand at 1000, and you have 100 units in inventory. You want 1000 x 115% = 1150 available for sale. Since you have 100 on hand, you would schedule 1050 for production.
If you cannot meet demand, sales go to competitors. Therefore, you want to plan for the upside as well as the downside. Your proforma balance sheet will forecast about eight weeks of inventory. You hope that your actual sales will fall between your sales forecast and the number of units available for sale.
Schedule production for your existing product using this formula:
(Unit Sales Forecast X 1.15) - Inventory On Hand.
New Product - Buy 500,000 units of capacity by entering 500 in the Buy Sell Capacity cell. Set an automation level of 2.0.
Important: There is a one year lag between purchase and use of new capacity and automation for both new and existing products.
Your fiscal policies should maintain adequate working capital reserves to avoid a liquidity crisis. Working capital can be thought of as the money that you need to operate day-to-day. In Foundation® working capital is current assets (cash + accounts receivable + inventory) - current liabilities (accounts payable + current debt). If you run out of cash because your sales are unexpectedly weak, an Emergency Loan will be issued.
Here are some guidelines to help you avoid an Emergency Loan . Your proforma balance sheet predicts your financial condition at the end of this year. Make conservative sales forecasts. Do not rely on the computer prediction. Override it with a forecast of your own. If you are conservative, it is unlikely that your worst expectations will be exceeded. Next, build additional inventory beyond your conservative expectations. This forces your proforma balance sheet to predict a future where your sales forecast comes true and you are left with inventory. (If you sell the inventory, that's wonderful.) On the Finance spreadsheet, issue stock, bonds or current debt until the December 31 Cash Position for the upcoming year equals at least five percent of your assets, as displayed on the proforma balance sheet. This creates an additional reserve for those times when your worst expectations are exceeded and disaster strikes.
As you gain experience with managing your working capital, you will observe that the guidelines above make you somewhat "liquid," and you may wish to tighten your policy by reducing cash and inventory projections. That is fine. The better your marketing forecasts, the less working capital you will require.
Cover the cost of your plant investment with equal amounts of long-term bond and stock issues.
Do not pay a dividend.
Save decisions (select "directly to the website").
Daze - Improve positioning and reduce age. Example: Increase Daze's performance to 7.0, reduce size by 13.0.
First New Product - Note that the new product's row is yellow instead of green, and that you cannot change these cells. This is because your product will not emerge from R&D until its current project completes. Under the rules of the simulation, new R&D projects cannot begin until the old one completes.
Second New Product - Launch a second new product places in both the Low Tech and, with a project length less than 2 years (no later than December of next year). Example: Name: Dude (replace the first NA in the list), performance 9.1, size 10.9 and a reliability (MTBF) 21000.
Important: Make certain the Daze project completes during this year, before December 31st. Under the rules, a new project can only begin on January 1st. If a project does not complete before the end of this year, you cannot begin follow-up project next year.
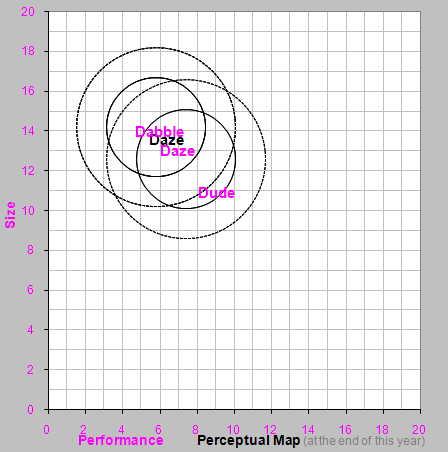
Daze - Hold price, promotion and sales budgets at current levels. Forecast unit sales near last year's level. Example: Price $34.75, promotion budget $1150, sales budget $1150, and sales forecast 1200.
First New Product - Enter promotion and sales budgets of $1150, and a price of $35.00. The product will not be released by R&D until after the first of the year, therefore enter a sales forecast of 500.
Second New Product - Marketing decisions will be made next year when the product is ready to begin production.
Schedule production using the formula:
(Unit Sales Forecast X 1.15) - Inventory On Hand
Important: As your new product is coming out sometime during the year, you might not be able to use the above formula - new products cannot begin production prior to their revision (release) date. Should the number you enter into the production schedule turn red, reduce the schedule until the red number turns black.
First New Product - Increase automation to 3.0.
Second New Product - Buy 500,000 units of capacity by entering 500 in the Buy Sell Capacity cell. Set an automation level of 2.0.
Match your plant investment with a stock issue. If you cannot raise adequate capital to match the investment, issue bonds to cover the shortfall.
Look at the proforma balance sheet, and add together your cash and inventory accounts. Apply the following rule of thumb. Keep between 15% and 20% of your balance sheet assets in cash plus inventory. You do not care about the mix, but you do want to have adequate reserves to cover unexpected swings in inventory.
Adjust your cash position to meet the above guidelines. If you are cash poor, issue additional stock or additional bonds. If you are cash rich, pay dividends.
Save decisions (select "directly to the website").
Daze - Improve positioning and reduce age. Example: Increase Daze's performance to 7.8 and reduce size to 12.2.
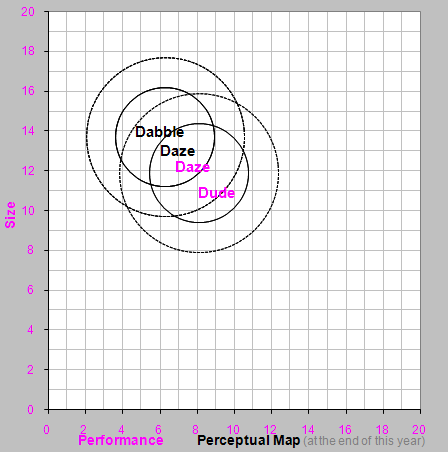
Daze - Change Daze 's promotion and sales budgets to $1200, and a price of $35.00. Forecast unit sales near last year's level. Enter a sales forecast of 1200.
First New Product - Enter promotion and sales budgets of $1200, and a price of $34.00. Enter a sales forecast of 900.
Second New Product - Enter a promotion and sales budget of $1000, and a price $45.00. The product will not be released by R&D until late in the year, therefore enter a sales forecast of 200.
For each product, schedule production using the formula:
(Unit Sales Forecast X 1.15) - Inventory On Hand
Important: As your new product is coming out sometime during the year, you might not be able to use the above formula - new products cannot begin production prior to their revision (release) date. Should the number you enter into the production schedule turn red, reduce the schedule until the red number turns black.
Follow the guidelines from last round to manage your cash position.
If you are cash poor, issue additional stock or additional bonds. If you are cash rich, pay dividends and retire stock.
Save decisions (select "directly to the website").
Your instructor may want you to play another practice round. If so, continue the Broad Differentiation vision.
Having executed the plan for two or three rounds, you are now in a position to analyze it. Consider the following questions:
What are this plan's strengths? Weaknesses?
How will competitors respond to your actions?
How can you influence competitors to avoid competing with you directly?
Which performance measures support this plan?
What is the long range potential of this plan? Its future sales volume? Its future profitability?
How can you best coordinate this plan as a team?